EFFICACY TESTING
Home » Solutions / Preclinical EEG Services / Preclinical Assays / Drug Efficacy Testing
Inform your Go/No Go Decision for the Clinic from the Preclinical Stage
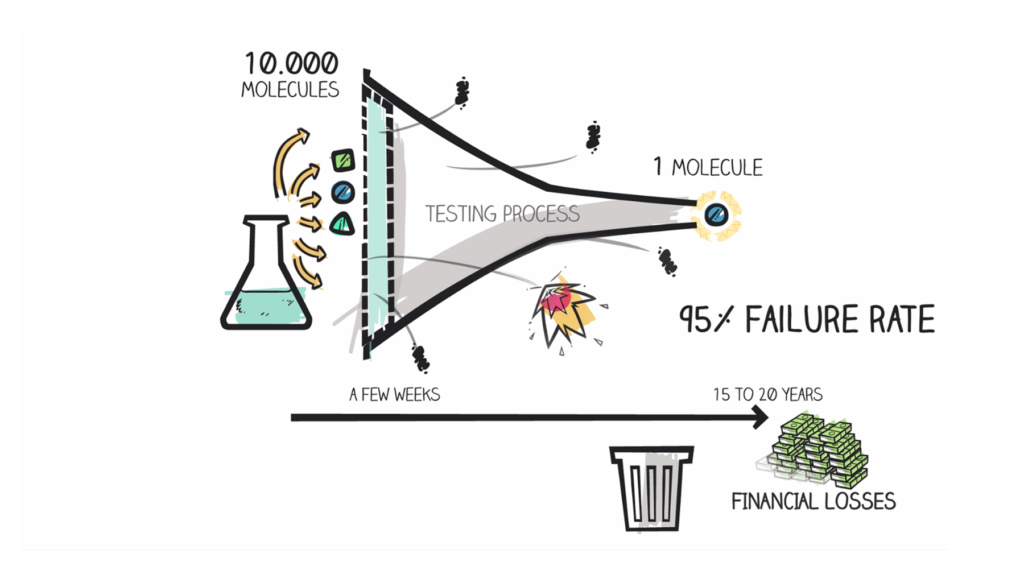
In today’s context, most drug candidates that make it to clinical trials will fail during efficacy testing, in Phase 2. This phase, when the efficacy of compounds is tested in patients, currently represents the most significant hurdle in drug development.
In order to improve success rates during Phase 2, it is important to act as early as possible during drug discovery. Ruling out unpromising candidates as early as the preclinical stage saves time and money, while allowing you to focus your efforts on the drugs that have the highest potential to demonstrate efficacy in clinical trials. To obtain these types of data, you will need a clinically-relevant preclinical model, a translational, reliable and robust biomarker, and a study design closely mirroring the clinical standard.
Associating pharmaco-sensitive EEG biomarkers with relevant in vivo rodent models, SynapCell aims to provide data to fuel decision-making.
Unique Expertise and Dedication in Preclinical EEG to Drive CNS Drug Discovery
Combining EEG biomarkers with translational in vivo rodent models of CNS disorders is central to SynapCell’s technology. We select our models based on reports in the literature and clinical observations, we also make sure that the associated EEG biomarkers are responsive to the standard of care used for the specific diseases modelled. In addition, our Neuroscientists perform a thorough analysis, allowing us to provide a complete set of preclinical data. Our Sponsors can thus fully inform their GO/NO-GO decision(s) on taking their compound(s) forward.
EEG Biomarkers: Translational Readout
One of the key features of our efficacy-testing models is their translational features. All of the EEG biomarkers in our portfolio have been shown to accurately represent clinical and patient outcomes.
We believe that the data we provide will give you insights in Phase 1 & 2 of clinical trials.

Relevant Study Design
SynapCell proposes standard designs such as crossovers to test acute conditions.
However, we do understand that tailored study designs may be needed to answer YOUR scientific question. We therefore provide bespoke study protocols based on comprehensive discussions to design the study that best meets your needs.

Experience and Expertise
We do not only provide high-level scientific results, our team of experts is also available for discussion before, during and after the study.
A discussion is systematically scheduled when results are delivered, to improve contextualization and help you to fully understand the data in hand. Our scientists will also bring to the table their experience with the different models, designs, and pharmacology, allowing you to get the most out of your study.
“Data from animal models are essential in predicting the clinical outcome for a specific drug in development.”
Denayer et al., 2024
Explore Efficacy Testing in our Therapeutic Areas
Familiarize yourself with our model of drug-resistant epilepsy: the MTLE mouse model. This model is adapted to screening, dose-response, chronic and anti-epileptogenesis studies. The MTLE mouse is a non-convulsive model, primary endpoints are the number of focal seizures, restricted to the hippocampus.
Our model of generalized absence epilepsy rat is bred from Wistars, which exhibit spontaneous, recurrent generalized absence epilepsy, known as Spike-and-wave discharges (SWD). SWD respond to the pharmacology used in the clinic, making this model a gold standard for this indication. Find out more about how to spot and quantify absence seizures using EEG with this model.
The most recent model developed at SynapCell is the amygdala kindling rat. This single model combines the characteristics of focal and non-convulsive seizures with those of secondarily generalized and convulsive seizures. It can be used to study a compound’s mechanism of action as well as its effect on different types of seizures.
The 6-OHDA rat model is a well-known preclinical model for Parkinson’s disease. SynapCell uses the translational features of EEG to shed light on functional CNS deficits. The pharmacology and the deficits found in the 6-OHDA rat mirror those reported for humans in the clinic.
Learn more…
Using the 6-OHDA model, we can replicate the L-Dopa-Induced Dyskinesia (LID) observed in patients following treatment with the drug. The corresponding EEG biomarker is specific to this condition and differs from that produced by PD itself. Find out more about this specific condition and its EEG biomarker.
This harmaline-induced model displays the deficits specific to essential tremor for a few hours after the acute injection. The biomarker induced by the injection of harmaline is reversible by propranolol, the standard of care for essential tremor. Find out more about the model and its pharmacological validation.
Recently, we identified two EEG biomarkers in an animal model of Fragile X Syndrome (FMR1 KO rats), based on qEEG analysis and 40-Hz ASSR. These two endpoints were significantly different between the WT and the transgenic animals. Based on the robustness of the differences, we now offer these EEG biomarkers as efficacy endpoints for compound testing.
Tau hyperphosphorylation is best known as one of the hypotheses for AD, but it is also implicated in many other CNS disorders. With the aim of providing a reliable drug development endpoint for these disorders, we developed the P301L model and applied our EEG technology.
Within the neuropsychiatric space, NDMA antagonists are commonly used to mimic CIAS deficits. Find out more about our MK-801 & ketamine assay and the auditory evoked potentials that serve as biomarkers for this condition.
Yohimbine (α-2 adrenergic antagonist) is used to mimic the acute effects of stress/anxiety in this rodent model. The effects observed – increased locomotor activity and EEG activity – are reversible with diazepam and other anxiolytic compounds.

Powered by Cue®, SynapCell's Predictive In Vivo EEG Platform
SynapCell’s rodent models and their associated EEG biomarkers are processed on Cue®, our innovative translational in vivo EEG platform, which is designed to predict the in-human efficacy of your drug candidates during the preclinical step. Cue® is the result of decades of R&D, combining SynapCell’s know-how, expertise and scientific excellence in the fields of brain surgery and EEG signal recording, processing, and analysis.
Using Cue®, we transform preclinical data into actionable insights, offering end-to-end support for informed decision-making in CNS drug discovery.
Let's Talk About Your Research Project!
More than a CRO, a team of collaborators – we are your dream neuroscience team specialized in preclinical EEG! We don’t just produce data, we are your partners from conceptualization to conclusion. We translate raw EEG data into meaningful, clinically-relevant endpoints, delivering clear insights to allow data-based decision-making. Choose SynapCell, a leading preclinical CNS-specialized CRO for cutting-edge EEG expertise combined with an irresistible touch of fun.
News & Events
PRESS RELEASE
SynapCell and the University of Utah Celebrate the 10-year Anniversary of their Collaboration on Anti-Seizure Medications.
NEW!
AMYGDALA KINDLING MODEL
Choose our Amygdala Kindling model to test compounds targeting focal-to-bilateral tonic-clonic seizures. Choosing the right model for the appropriate type of epilepsy seizures is key to the effective discovery of ASMs.
NEW!
SLEEP & VIGILANCE STATES
Discover SynapCell’s new preclinical EEG capabilities for sleep and vigilance states, and gain additional insights to characterize compound effects.

