Welcome to
synapcell blog
Home » Resources / Blog / BetaPark-Translational EEG Biomarker
What is BetaPark?
BetaPark is a translational EEG biomarker recorded in the motor cortex of both PD patients and animal models of prodromal and late-onset PD. Suppressed by dopaminergic drugs, BetaPark is used to quantify the efficacy of therapies against PD.
Breaking it down:
Motor symptoms observed in Parkinson’s Disease result from a dysfunction of the cortico-basal ganglia circuits mainly due to the progressive depletion of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta.
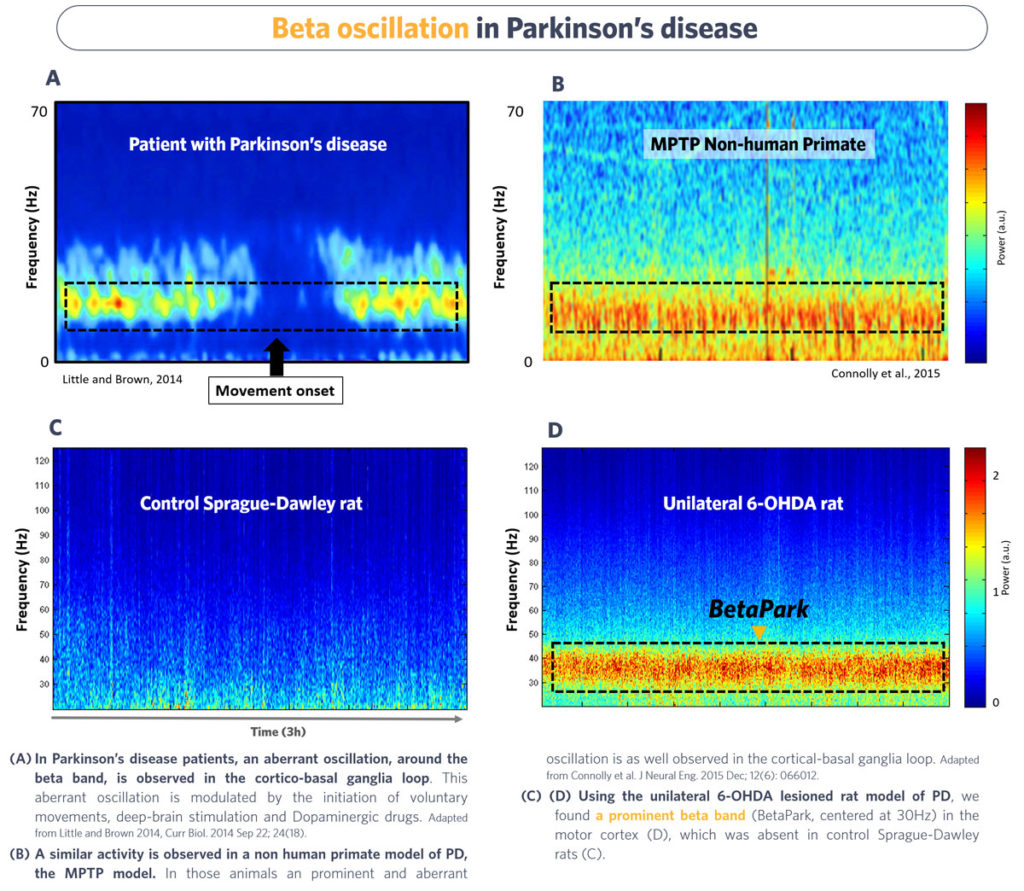
Accumulative evidences have demonstrated the presence of aberrant hypersynchronization of beta frequency oscillatory activity in these circuits in both parkinsonian patients (Little and Brown, 2014) and experimental animal models of the disease.
These beta activities have been correlated with symptoms such as hypokinesia and rigidity (Hammond et al., 2007, and Little et al., 2012). Treatments with dopaminergic drugs and deep brain stimulation reduce and even transiently suppress these pathological oscillations and are known to improve the motor symptoms (Hammond et al., 2007).
Pogosyan et al. (2009) also demonstrated the causality between any physiological oscillatory brain activity and concurrent motor behavior in the healthy human and that boosting cortical activity at beta frequency was slowing movement in human. This work helps explain how the exaggerated beta activity found in Parkinson’s disease can lead to motor slowing in this neurodegenerative disorder.
Animal models of PD such as the MPTP non-human primate (Connolly et al., 2015), the unilateral 6-OHDA-lesioned rat (mimics PD late stage), or the bilateral AAV-alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) rat model show a prominent cortical beta activity that is significantly lowered by dopaminergic drugs, making them clinically-relevant for the evaluation of anti-PD therapies.
BetaPark is a perfect biomarker for the investigation of the two main phases of the disease: the prodromal and the symptomatic phase.
- First, BetaPark allows to measure the efficacy of neuroprotective agents over several weeks in freely moving AAV-alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) rat.
- Then, BetaPark precision allows for a range of accurate pharmacodynamic studies able to deliver decision-making information with the unilateral 6-OHDA-lesioned rat.
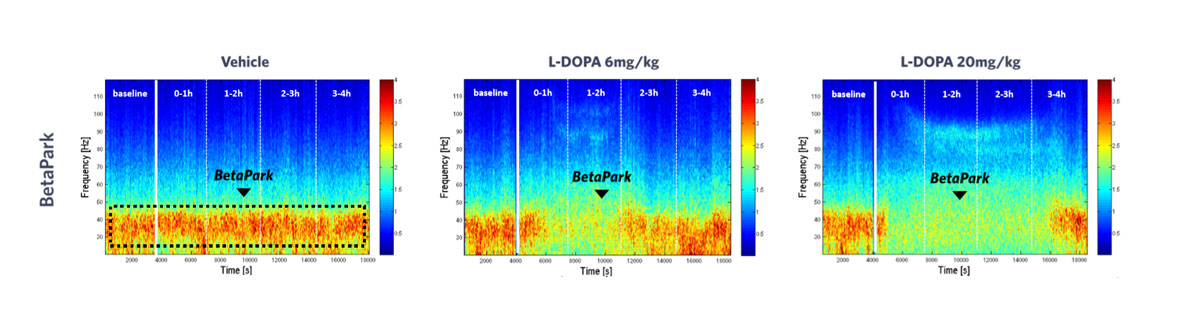
Dopaminergic agonists transiently silence BetaPark.
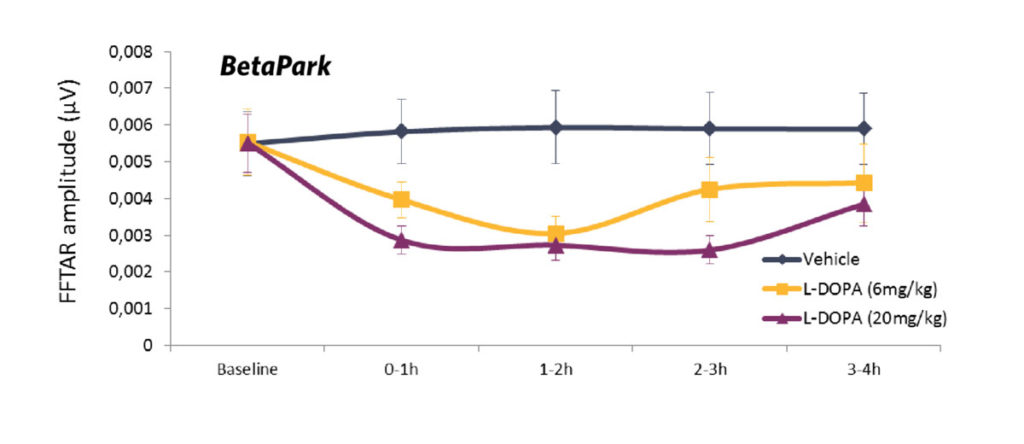
Pharmacosensitive and stable over time, BetaPark is dose-dependently lowered by the dopamine replacement therapy L-DOPA. The higher the L-DOPA dose, the more intense and longer effect in lowering BetaPark.
BetaPark is exclusively identified by SynapCell’s state-of-the-art EEG methodologies in preclinical and clinically-relevant models of PD: in the 6-OHDA rat and in the AAV-alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) rat (undisclosed ongoing collaboration – data not shown)
BetaPark represents a predictive, reliable, objective and translational biomarker of early and late phases of PD.
BetaPark therefore presents all the features that makes it a surrogate biomarker for the identification of new treatments against PD or the validation of disease modifying experimental therapeutics.
At Synapcell, we are proud to propose a full range of possibilities to address all stages of Parkinson’s disease, with a level of predictivity that’s unique on the market.
Head to our Parkinson’s Page for a deeper look on BetaPark, L-DOPA induced GammaPark* and contact us to dig into the data!
* L-DOPA induced GammaPark :
In Parkinson’s disease, motor dysfunctions are thought to be related to an imbalance between antikinetic beta band (13-30 Hz) rhythms and prokinetic gamma band (60-90 Hz) rhythms in the motor network. Chronic treatment with L-DOPA suppresses antikinetic beta band rhythms (BetaPark) while promoting cortical oscillations in the gamma frequency band (GammaPark), that correlate to L-DOPA induced dyskinesia. GammaPark is a prefect biomarker for the investigation of therapeutical strategies against Dyskinesia.
Chronic treatment with L-DOPA leads to the rise of resonant cortical oscillation in the gamma frequency band (GammaPark), that correlate to L-DOPA induced dyskinesia.
Learn more about oscillatory activities in Essential Tremor.